Tornar
Hepatic ablation using radiofrequency
In recent years, radiofrequency (RF) ablation has become a promising, minimally invasive therapy for treating malignant liver tumours. However, the limited volume of ablation possible, in addition to the predictability and adaptation to a particular tumour, is still an obstacle hindering the wider application of this therapy. We have developed a new electrode (Gnomon) that incorporates a unique internal cooling system and a hypersaline solution infusion system.
This device should prevent the saline solution boiling, the tissue carbonising, and improve the electrical conductivity, leading to larger and more predictable ablations that better match the geometry of the tumour. We have recently completed a clinical trial with 70 patients in the Hospital del Mar (http://www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN73194360) aimed at evaluating the effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation using this device and microwave thermal ablation in the treatment of liver tumours. .

Figura 1. Diagram of the hybrid applicator that includes an internally cooled electrode and two small diameter expandable tubes for perfusing hypertonic saline (20% NaCl) into the tissue at 6 mL/h.
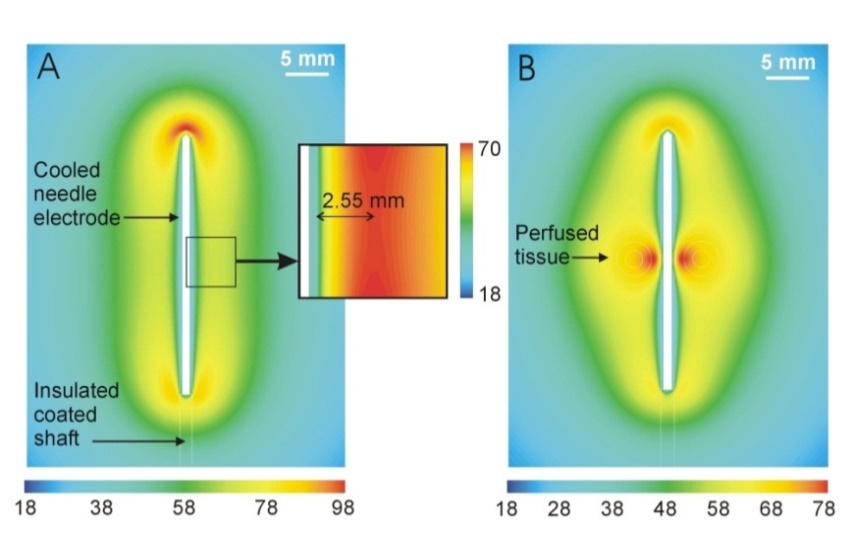
Figura 2. Computational analysis (Finite Element Model) of the temperature reached in the tissue at the end of the ablation in a conventional internally cooled ablation system (A) and in our ablation system (B). The green (around 50°C) shows the estimated volume of the final ablation. In our ablation system (B), hypersaline solution is introduced to improve the shape and size of the ablation, making it larger and more spherical.
Important publications
- Trujillo M, Bon J, José Rivera M, Burdío F, Berjano E. Computer modelling of an impedance-controlled pulsing protocol for RF tumour ablation with a cooled electrode. Int J Hyperthermia. 2016 Dec;32(8):931-939. Epub 2016 Jul 24. González-Suárez A, Trujillo M, Burdío F, Andaluz A, Berjano E. Could the heat sink effect of blood flow inside large vessels protect the vessel wall from thermal damage during RF-assisted surgical resection? Med Phys. 2014 Aug;41(8):083301. doi: 10.1118/1.4890103.
- González-Suárez A, Trujillo M, Burdío F, Andaluz A, Berjano E. Feasibility study of an internally cooled bipolar applicator for RF coagulation of hepatic tissue: experimental and computational study. Int J Hyperthermia. 2012;28(7):663-73. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2012.716900.
- Romero-Méndez R, Tobajas P, Burdío F, Gonzalez A, Navarro A, Grande L, Berjano E. Electrical-thermal performance of a cooled RF applicator for hepatic ablation with additional distant infusion of hypertonic saline: in vivo study and preliminary computer modeling. Int J Hyperthermia. 2012;28(7):653-62. doi: 10.3109/02656736.2012.711894.
- Burdío F, Tobajas P, Quesada-Diez R, Berjano E, Navarro A, Poves I, Grande L. Distant infusion of saline may enlarge coagulation volume during radiofrequency ablation of liver tissue using cool-tip electrodes without impairing predictability. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011 Jun;196(6):W837-43. doi: 10.2214/AJR.10.5202.
- Burdio F, Mulier S, Navarro A, Figueras J, Berjano E, Poves I, Grande L. Influence of approach on outcome in radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. Surg Oncol. 2008 Dec; 17(4):295-9. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2008.03.002.
- Burdío F, Navarro A, Sousa R, Burdío JM, Güemes A, Gonzalez A, Cruz I, Castiella T, Lozano R, Berjano E, Figueras J, de Gregorio MA. Evolving technology in bipolar perfused radiofrequency ablation: assessment of efficacy, predictability and safety in a pig liver model. Eur Radiol. 2006 Aug;16(8):1826-34.
- Burdio F, Navarro A, Sousa R, Guemes A, Burdio JM, Tejero E, Lozano R. Premature roll-off in radiofrequency ablation using bipolar saline-enhanced electrodes. Eur Radiol. 2005 Jul;15(7):1495-6; author reply 1497-8.
- Burdío F, Burdío JM, Navarro A, Ros P, Güemes A, Sousa R, Tejero E, Lozano R. Electric influence of NaCl concentration into the tissue in radiofrequency ablation. Radiology. 2004 Sep;232(3):932; author reply 932-3.
- Burdío F, Güemes A, Burdío JM, Navarro A, Sousa R, Castiella T, Cruz I, Burzaco O, Lozano R. Bipolar saline-enhanced electrode for radiofrequency ablation: results of experimental study of in vivo porcine liver. Radiology. 2003 Nov;229(2):447-56.


